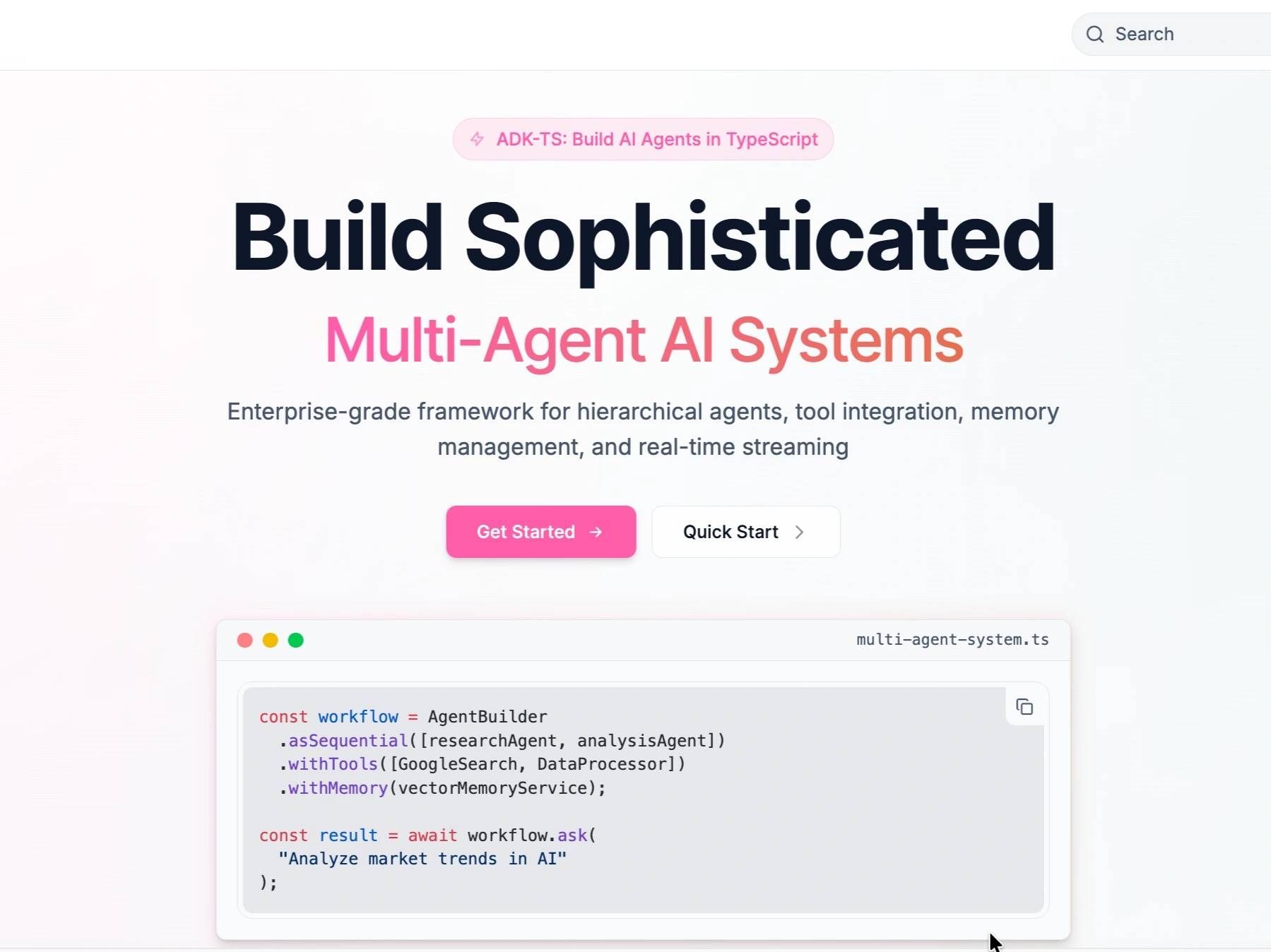
ADK for TypeScript
Agent Development Kit (ADK) for TypeScript is an open-source framework created by IQ AI for the development, orchestration, and deployment of intelligent AI agents. It provides a TypeScript-first toolkit for building a range of AI systems, from simple question-and-answer bots to complex multi-agent architectures capable of performing real-world tasks, with a focus on type safety and modularity [1] [3].

Overview
The Agent Development Kit (ADK) for TypeScript is a framework that enables developers to construct multi-agent AI systems. Inspired by Google's Python ADK, it adapts the architecture for the TypeScript ecosystem, focusing on type safety, modularity, and developer experience. The kit supports hierarchical agents, integrates various tools, manages memory, and handles real-time streaming. Its role encompasses the building, orchestration, and deployment of AI agents [2] [4]. Launched on July 17, 2025, ADK for TypeScript supports developers in building AI agents [1].
ADK for TypeScript functions as a toolkit for creating diverse AI applications. Its design considers developer experience, offering features like autocompletion and type safety inherent to TypeScript. The framework's modular architecture allows for composition of agents, attachment of various tools, and integration with multiple large language models (LLMs) [1]. It is designed to scale from prototypes to production deployments, incorporating functionalities such as session management, persistent memory, and OpenTelemetry support for tracing and performance monitoring [2].
Key Features
ADK for TypeScript is built around several core features that support its use for developers. These features contribute to its capability to support AI agent development.
AgentBuilder API
The AgentBuilder API is a component designed for the rapid creation and configuration of AI agents using a fluent, chainable interface. It simplifies development by automatically handling session creation, memory management, and configuration defaults, allowing developers to focus on agent logic. While direct instantiation of agents offers maximum control for production systems, AgentBuilder is optimized for quick prototyping and building multi-agent workflows [8].
Key functionalities include:
- Fluent API: Uses a chainable method structure (e.g.,
.withModel().withTools().build()) for intuitive configuration. - Automatic Session Management: Manages in-memory sessions for conversation state by default, which can be replaced with persistent solutions.
- Smart Defaults: Provides sensible default configurations to reduce boilerplate code for common use cases.
- Multi-Agent Orchestration: Includes built-in methods to create complex multi-agent systems with sequential, parallel, loop, or graph-based execution patterns.
The API supports various configuration methods for core settings, input/output schemas, tools, session management, and execution hooks. Terminal methods like .build() construct the agent, while convenience methods like .ask(message) build and immediately execute the agent with a single query [8].
Model and Provider Integration
The framework offers a flexible system for integrating a wide range of large language models (LLMs). While it defaults to Google's Gemini models, it supports two primary methods for using other providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Groq [9].
- Direct Model Names: A straightforward method where a model's string identifier (e.g.,
gpt-4o) is passed to the agent. This requires setting environment variables likeLLM_MODELand the provider-specific API key (e.g.,OPENAI_API_KEY). This approach is suitable for quick setups and production applications with fewer dependencies. - Vercel AI SDK Integration: A more advanced approach that uses model instances from the Vercel AI SDK. This method offers greater control, access to a wider range of providers with a consistent API, and advanced features like streaming. It is recommended for multi-provider setups and for using local or open-source models via integrations like
@ai-sdk/ollama.
The following providers are supported through these methods [9]:
| Provider | Example Model Names | Required Environment Variable |
|---|---|---|
| Google Gemini | gemini-2.0-flash, gemini-2.0-pro, gemini-1.5-pro | GOOGLE_API_KEY |
| OpenAI | gpt-4o, gpt-4, gpt-3.5-turbo | OPENAI_API_KEY |
| Anthropic | claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022, claude-3-opus | ANTHROPIC_API_KEY |
| Groq | llama-3.1-70b-versatile, mixtral-8x7b | GROQ_API_KEY |
| Mistral | mistral-large-latest, codestral-latest | MISTRAL_API_KEY |
Modular Architecture and Tool Integration
ADK for TypeScript features a modular architecture that enables developers to compose agents and integrate various tools. Developers can compose multiple agents, equip them with custom tools, and orchestrate workflows. Agents can be equipped with ready-to-use tools or custom-built functionalities. Tool integration is facilitated via the Model Context Protocol (MCP), which supports tooling, function integration, and automatic schema generation, allowing connection to a range of MCP servers in the market or the creation of custom ones. This modularity provides developers with options in designing and extending their AI systems [2] [4].
Memory Management and Session Handling
The kit includes features for stateful memory and session management, allowing agents to maintain context and state across multiple interactions or sessions. This is for building AI assistants and autonomous agents that require persistent knowledge and continuity in their operations. Built-in session management and memory services are designed for enterprise deployment, supporting reliability and scalability [1] [4].
Tracing and Evaluation
ADK for TypeScript incorporates OpenTelemetry support for tracing and performance evaluation. This allows developers to debug agent behavior, monitor performance metrics, and gain insights into the execution flow of multi-agent systems. The tracing capabilities support optimizing agent performance and reliability in production environments. Additionally, it includes a built-in evaluation system to assess agent performance by testing final responses and execution trajectories [1] [4].

Agents
Agents are the central abstraction in ADK for TypeScript. They are designed to encapsulate AI models, instructions, tools, and coordination logic, creating autonomous programs that can interpret instructions and execute complex tasks [4].
Agent Types
ADK for TypeScript offers several types of agents, each suited for different use cases, allowing developers to build sophisticated systems by combining them [4].
-
LLM Agents: These are the most common agent type, utilizing large language models for reasoning, decision-making, and tool usage. They form the core of conversational AI and task-oriented bots.
-
Workflow Agents: These agents are designed to orchestrate other agents in structured patterns. They include several sub-types:
- Sequential Agents: Execute a series of sub-agents in a predefined order, suitable for predictable, step-by-step workflows and data processing pipelines.
- Parallel Agents: Run multiple agents or tasks simultaneously, which is ideal for improving performance by processing independent tasks concurrently.
- Loop Agents: Repeatedly execute an agent or a workflow until a specific condition is met. This is useful for iterative processes, retry logic, or tasks that require continuous refinement.
-
Custom Agents: The framework allows for the creation of specialized agents with custom logic and behavior. This enables developers to build agents tailored to specific needs or integration patterns that are not covered by the standard agent types.
-
Multi-Agent Systems: ADK supports the coordination of multiple agents to solve complex, distributed problems. This allows for the creation of systems where specialized agents collaborate, each handling a different aspect of a larger task.
These agent types provide a flexible foundation for building a wide range of AI applications [4].
Choosing the Right Agent Type
The selection of an agent type depends on the specific requirements of the task. The framework provides a guide for choosing the most appropriate agent for a given scenario [4].
- LLM Agents are best for tasks requiring reasoning, conversation, and dynamic tool usage.
- Sequential Agents should be used for step-by-step workflows and pipelines where the order of operations is critical.
- Parallel Agents are ideal for independent tasks that can be executed simultaneously to enhance speed and efficiency.
- Loop Agents are perfect for implementing iterative improvement, polling, or retry logic.
- Custom Agents are necessary when a project requires specific behaviors or integration patterns not available out-of-the-box.
- Multi-Agent Systems are suited for complex problems that benefit from the coordination of multiple specialized agents.
This guidance helps developers architect more effective and efficient AI systems [4].
Multi-Agent Workflows
ADK for TypeScript provides robust support for orchestrating multi-agent workflows, enabling teams of specialized agents to collaborate on complex tasks. The framework's AgentBuilder API facilitates the creation of these workflows through several built-in orchestration patterns. Developers can design sequential pipelines, run agents in parallel, create iterative loops, or build complex, graph-based systems with conditional branching. This allows for the creation of sophisticated AI systems where agents can delegate tasks and work together to achieve a common goal [8].
x402 Protocol Integration for On-Chain Payments
ADK-TS integrates with Coinbase's x402 protocol, an open standard designed to facilitate on-chain crypto payments for AI agents and other digital services. This integration enables developers to build agents that can automatically charge for their services and pay for API calls using crypto micropayments, creating a foundation for autonomous, monetized AI economies [6].
The x402 protocol is based on the HTTP 402 Payment Required status code. The process involves a server responding to a request for a paid resource with a 402 error, which specifies the cost, currency (e.g., USDC), and destination address. The client then makes the payment on-chain and retries the request, including cryptographic proof of payment in the X-PAYMENT header. The server verifies this proof and grants access to the resource. This system supports instant, global micropayments, which are often impractical with traditional payment methods like credit cards [6].
ADK-TS x402 Agent Template
To demonstrate this capability, IQ AI released the ADK-TS x402 agent template. This starter project provides developers with a complete setup for building AI agents with native crypto payment functionality. The template is structured into three key components that work together [6]:
- The Server: Acts as an x402 paywall proxy. It defines which API routes are free and which are paid, enforces pricing, and verifies on-chain payments before forwarding requests.
- The Agent: Built with ADK-TS, the agent is designed to use both free tools (like checking API prices) and paid tools for premium features. It can inform the user of the cost of an action and request approval before proceeding with a payment.
- The Client: Utilizes axios middleware integrated with a crypto wallet to handle the 402 payment challenges. It automates the process of making on-chain payments and retrying requests with the necessary proof.
A key architectural feature of the template is the separation of concerns: pricing and payment logic reside on the server, not within the agent's code. This allows developers to update pricing without needing to redeploy the agents and keeps the agent's logic focused on its core tasks. The template runs on the Base Sepolia testnet, allowing for experimentation without real funds [6].
This integration of ADK-TS intelligence with x402 economics supports the development of new models for AI, such as pay-per-API call services, marketplaces where agents transact with each other, and decentralized agent economies where agents can earn and spend autonomously [6].
Integration with NEAR Protocol
ADK-TS integrates with the NEAR Protocol to enable the creation of autonomous AI agents that can securely execute transactions on-chain without human intervention. This is achieved through a collaboration with NEAR Shade Agents, which combine AI intelligence with secure blockchain execution [7].
ADK-TS and NEAR Shade Agents
The integration pairs the AI capabilities of ADK-TS with the blockchain execution framework of NEAR Shade Agents. In this architecture, ADK-TS is responsible for the agent's intelligence, allowing it to monitor conditions, analyze data, and make decisions. NEAR Shade Agents handle the secure execution of blockchain transactions [7].
A key challenge in AI-blockchain integration is securely managing private keys for transaction signing. NEAR Shade Agents address this using Account Abstraction and Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs). Each AI agent is assigned its own NEAR account with private keys stored securely within a TEE, which provides hardware-level protection. This setup allows the agent to sign transactions autonomously. Furthermore, through NEAR's Chain Signatures technology, these agents can sign transactions not only on the NEAR blockchain but also on other chains like Ethereum and Bitcoin, enabling cross-chain operations [7].
Shade Agent Template
To facilitate development, a dedicated ADK-TS template, the "Shade Agent" template, is available. This template provides a practical example of an AI agent that monitors Ethereum market sentiment by analyzing Reddit headlines, fetches real-time price data from CoinGecko, and autonomously signs and broadcasts a transaction to update an on-chain oracle contract. The template includes pre-configured REST API endpoints for managing and interacting with the agent, allowing developers to monitor its NEAR and Ethereum accounts and trigger its transaction-signing process [7].
On-Chain Capabilities
For developers working within the Web3 ecosystem, ADK for TypeScript offers support for integrating with blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. This enables AI agents to interact with on-chain data and protocols.
These capabilities are supported by a suite of specialized Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers developed by IQ AI, designed to extend the capabilities of ADK TypeScript agents by providing integration with various external services and data sources.
Specific on-chain functionalities include:
- Analyzing DeFi positions on platforms such as Fraxlend and BAMM.
- Executing token swaps through decentralized exchange aggregators like ODOS.
- Managing tokenized agents on the Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP).
- Interacting with smart contracts directly via their Application Binary Interface (ABI).
- Bridging assets or information across different blockchain networks, including NEAR Protocol. These capabilities are supported by a suite of Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers for blockchain interaction, facilitating the creation of AI agents that can operate within decentralized environments [1].
MCP Servers
IQ AI has developed a collection of specialized Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers to enhance and extend the capabilities of ADK TypeScript agents. These servers provide integration with various external services and data sources. The available servers include:
- MCP ABI: For smart contract ABI interactions on Ethereum-compatible blockchains.
- MCP ATP: To interact with the IQ AI Agent Tokenization Platform.
- MCP BAMM: For Borrow Automated Market Maker operations on Fraxtal.
- MCP Discord: To interact with Discord bots and channels for messaging automation.
- MCP Fraxlend: For interacting with the Fraxlend lending platform.
- MCP IQWiki: To access and manage IQ.wiki data and user activities.
- MCP NEAR Agent: For NEAR Protocol blockchain integration with AI-driven event processing.
- MCP ODOS: To interact with decentralized exchanges through ODOS aggregation.
- MCP Telegram: For interacting with Telegram bots and channels for messaging automation.
- MCP Upbit: To interact with the Upbit cryptocurrency exchange for market data and trading.
This suite of servers enables developers to build agents with a wide range of on-chain and off-chain capabilities [4].
ADK-TS CLI
The ADK-TS Command Line Interface (@iqai/adk-cli) is a toolkit for AI agent development, testing, and deployment. It is built with TypeScript and NestJS and provides a development environment that covers the entire lifecycle from project creation to production deployment. The CLI is noted as an experimental feature, and its APIs may change in future releases [5].
Key Features
The ADK-TS CLI includes a range of features designed to support professional AI agent development [5].
Development & Testing
- Project Scaffolding: Generate new projects from pre-built templates for applications like Discord bots, web servers, and MCP servers.
- Interactive Chat Interface: A terminal-based chat interface with markdown rendering for rapid testing and interaction with agents.
- Web UI: A React-based graphical interface for visual agent management and testing.
- Hot Reload: Automatically reloads code during development when changes are detected, with customizable watch paths.
- Smart Agent Discovery: Automatically scans for agent files, respecting
.gitignorerules and allowing for path filtering.
Production & Deployment
- RESTful API Server: A full-featured HTTP server for managing agents and handling messaging in a production environment.
- OpenAPI Documentation: Automatically generates Swagger documentation for the ADK server's API endpoints.
- Health Monitoring: Includes built-in health checks and status endpoints for monitoring the application's state.
- Session Management: Provides persistent conversation sessions with state management capabilities.
- Event Streaming: Supports real-time event delivery via Server-Sent Events (SSE).
Developer Experience
- Multi-Package Manager Support: Automatically detects and supports npm, pnpm, yarn, and bun.
- Intelligent CLI UX: Features interactive prompts, spinners, and progress indicators to improve the user experience.
- Debug Mode: Offers comprehensive logging and diagnostics for troubleshooting.
- Cross-Platform: Fully supports Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems.
ADK-TS Hackathon 2025
In October 2025, IQ AI announced the winners of the four-week ADK-TS Hackathon 2025. The event attracted 122 builders who submitted 50 projects, with 34 qualifying for the final judging stage. The hackathon aimed to showcase the capabilities of the ADK-TS framework in building innovative AI agents [10].
Main Track Winners
Three projects were awarded $1,000 each in stablecoins for their excellence in core categories.
| Category | Project Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Agent Application | CodeForge AI | A multi-agent platform for end-to-end software development, including code generation, security scanning, and testing. |
| MCP Expansion | OpsPilot | A Discord-native AI on-call team for DevOps that monitors alerts, triages incidents, and generates pull requests to fix issues. |
| Web3/Blockchain Use Case | ChainInsight | An AI agent that manages DeFi workflows through conversation, including protocol research, transaction simulation, and risk analysis. |
Bonus Track and Noteworthy Winners
Thirteen other projects received awards of $200 each for their contributions in specialized areas. These included awards for Most Practical Real-World Use Case (Confluent, an accounting platform integrator), Best Bot Integration (BingeBird, a Telegram entertainment discovery bot), Best Technical Implementation (Obrix, a wash trading detection platform), and Best Improvement to ADK-TS (Bazaaro, an integration with Coinbase's CDP AgentKit). Other noteworthy projects focused on blockchain terminals, on-chain analytics, automated trading, and drug discovery [10].